The African tech scene is proliferating and has become a hub for innovative startups. This growth has resulted in increased demand for developers, which means higher salaries. Developer salaries in Africa vary greatly depending on the country, experience level, and type of job. Software developers can generally expect to earn anywhere from $20,000 to over $100,000 per year. Countries with higher GDPs tend to pay more for development jobs than those with lower GDPs.
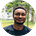
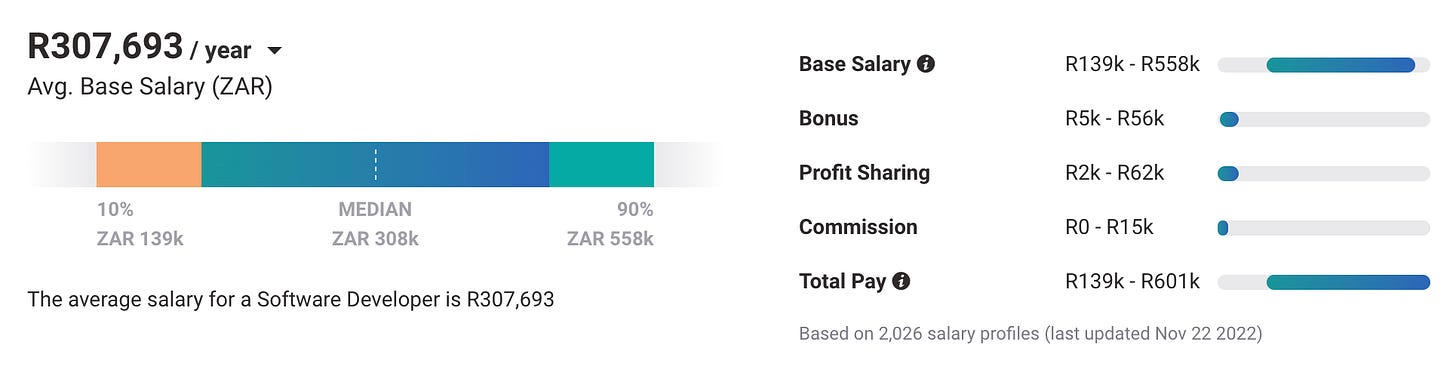
For example, a software developer in South Africa may make an average annual salary of around R300 000 ($17 500), while one in Nigeria could make NGN1.8 million ($4 000).
Interestingly, there is a significant income spread between the two countries between the highest earners and the average earners. For example, the biggest earners in SA make 1.7 times the average for that country, however, Nigeria’s more skilled developers earn 2.5 times the national average!
This gap can be a reflection of the different general salary levels in urban vs. rural areas or a fast-growing demand for software developers in that country that increases the demand for skilled staff. In addition to the different wages based on geography and experience level, other factors affect how much African developers can earn. Companies often use different payment structures for their staff such as bonuses or stock options which significantly increase potential earnings.
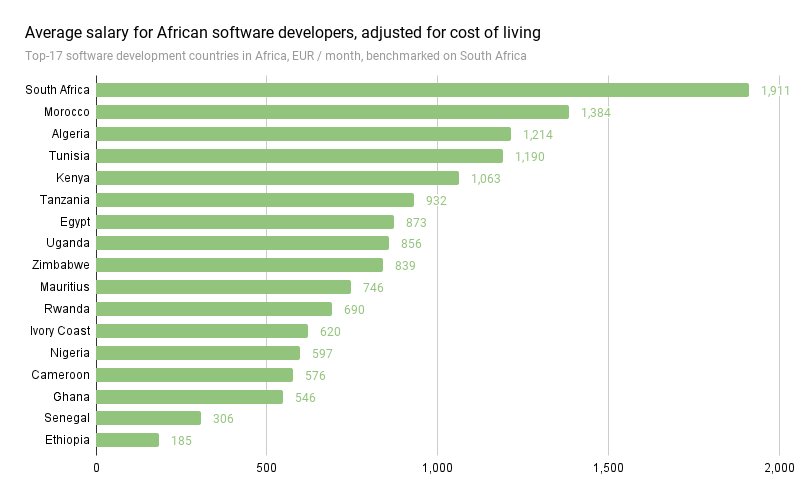
Although South Africa does pay the best, the cost of living can be expensive. That means the higher salary could become lower pay after the cost of living. The chart is arranged by Tunga, an information technology firm. The chart shows the countries on the bottom (Ethiopia, Senegal and Ivory Coast) as the least attractive, due to a high cost of living and low salaries. The prime locations are found top half: Morocco and Kenya. While the cost of living in South Africa is high, we can safely say that expenses are offset by the high salaries. The reverse seems true for Algeria, Tunisia, Egypt and Uganda. There, the cost of living is so low that it compensates significantly for the relatively lower salary level.
Despite the potential of high wages, there are still many challenges that African developers face. A lack of access to resources such as reliable internet and up-to-date technology can limit their ability to keep up with trends and stay competitive with their peers in other countries. Additionally, many companies do not offer benefits like health insurance or retirement plans which can make it difficult for developers to plan for the future.